A study by Alert Logic, a threat intelligence and defense company, lists the main weaknesses in attacks against more than four thousand clients.
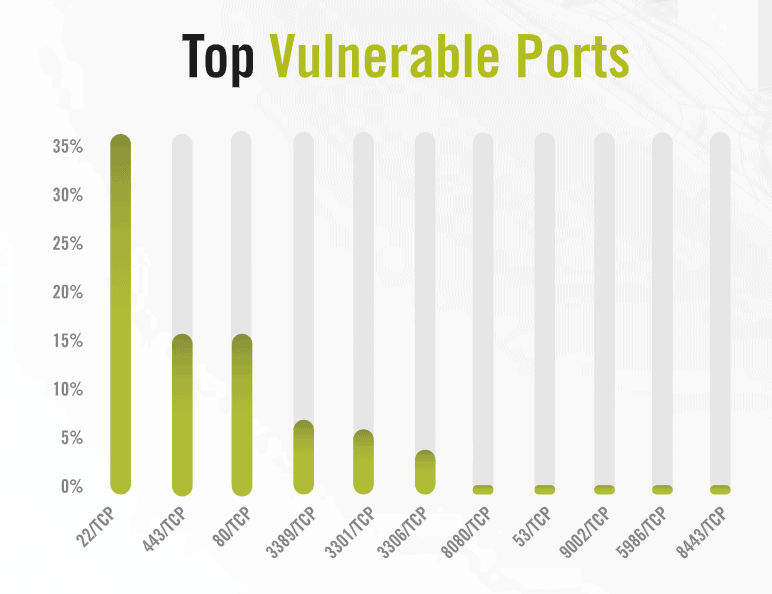
Top targeted TCP ports
The study states that 22, 80 and 443 ports most often used for the attack are SSH (Secure Shell), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Safe Hypertext Transfer Protocol). Alert Logic suggests that in 65 percent of events these appear and it makes sense because they must be accessible to interaction, secure or plain text. Fourth location is the port for the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) of Microsoft that is accountable for remote machine interaction. This year, RDP has been drawn to the attention of various patches for remote code implementation vulnerabilities (CVE-2019-1181, CVE-2019-1182 and CVE-2019-0708). “As basic guidance, security across all network ports should include defense-in-depth. Ports that are not in use should be closed and organizations should install a firewall on every host as well as monitor and filter port traffic. Regular port scans and penetration testing are also best practices to help ensure there are no unchecked vulnerabilities” – Alert Logic For the File Transfer Protocol (FTP–20, 21), a port is identified as a severe danger. On printers, cameras and continuous power supplies, which are estimated to be up to a third of all FTP servers discovered, active servers were found. The suggestion of the company to decrease prospective danger of such ports is to keep up-to-date, tough devices, software or services relying on these ports to close the paths of assault.
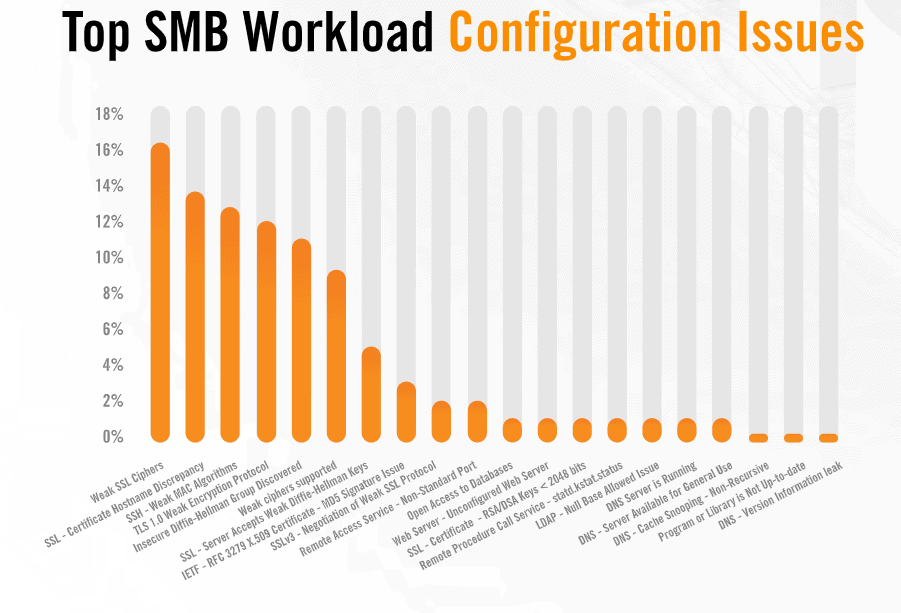
Old software running
Additional vulnerabilities to a company’s safety refer to the weak encryption and obsolete, 66 percent and 75 percent of the problems Alert Logic has noticed with its clients.
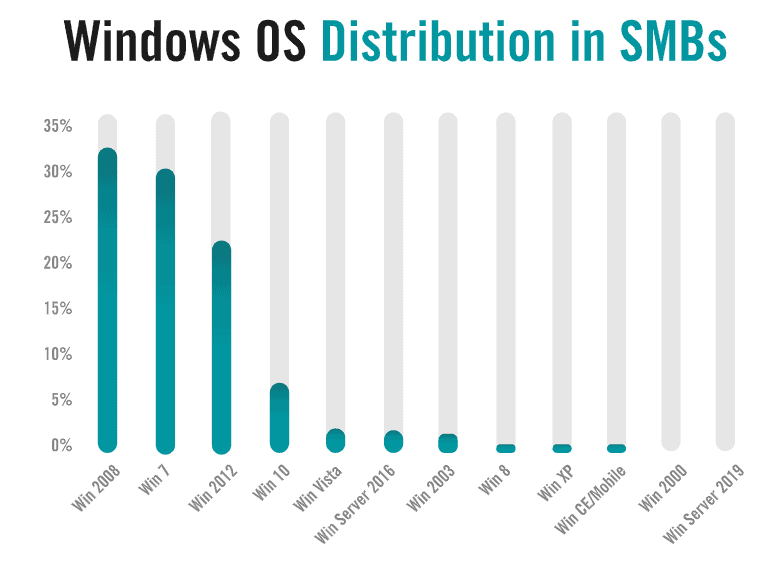
The problems continue as the company has determined that more than 66 percent of the scanned hosts run Windows 7, an OS that won’t be supported by 14 January 2020 any longer. Windows Server 2019 is scarcely visible on the infrastructure of SMBs. Windows XP, which ended in 2008 and ended in assistance in 2014, is still present in a’ non-trivial’ amount because of some reason. Alert Logic claims that he has even discovered Windows NT devices on the network of his clients (published in 1993). The danger of running them is that it will make the lateral movement of the attacker dead easy.
Nearly half of all Linux scanners had an obsolete kernel; more precisely version 2.6, which has been unavailable over the previous three years and has 65 recognized vulnerabilities upward. However, this problem is not as noticeable as deployed applications that conceal the underlying OS allocation.
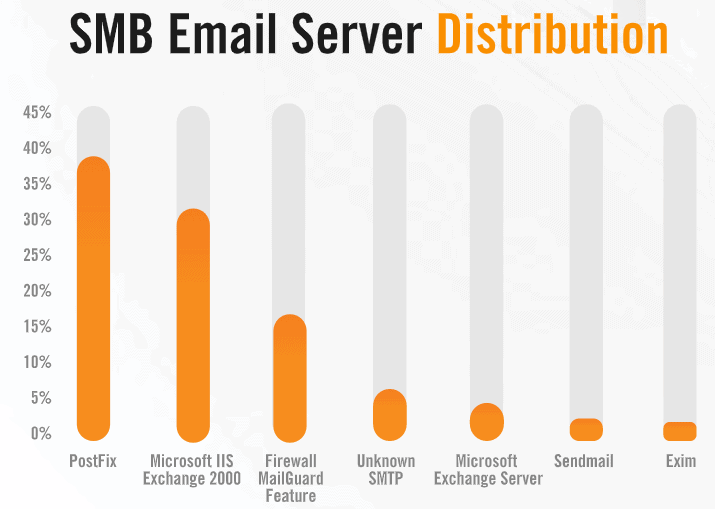
Another instance is the Exchange 2000 e-mail server, which accounts for nearly one-third of all identified e-mail servers. The problem is that the item was no longer supported in July 2010. The most common email server with the Alert Logic-monitored SMBs is PostFix, and the most widely used email server is Exim.
Alert Logic said that information were collected over a period of six months from 5,000 assaults daily on its client base, from November 2018 to April 2019.